TNUoS charges depend on the grid connection, asset size, and duration
Embedded export tariffs
These tariffs only apply to distribution-connected batteries with a capacity below 100MW.
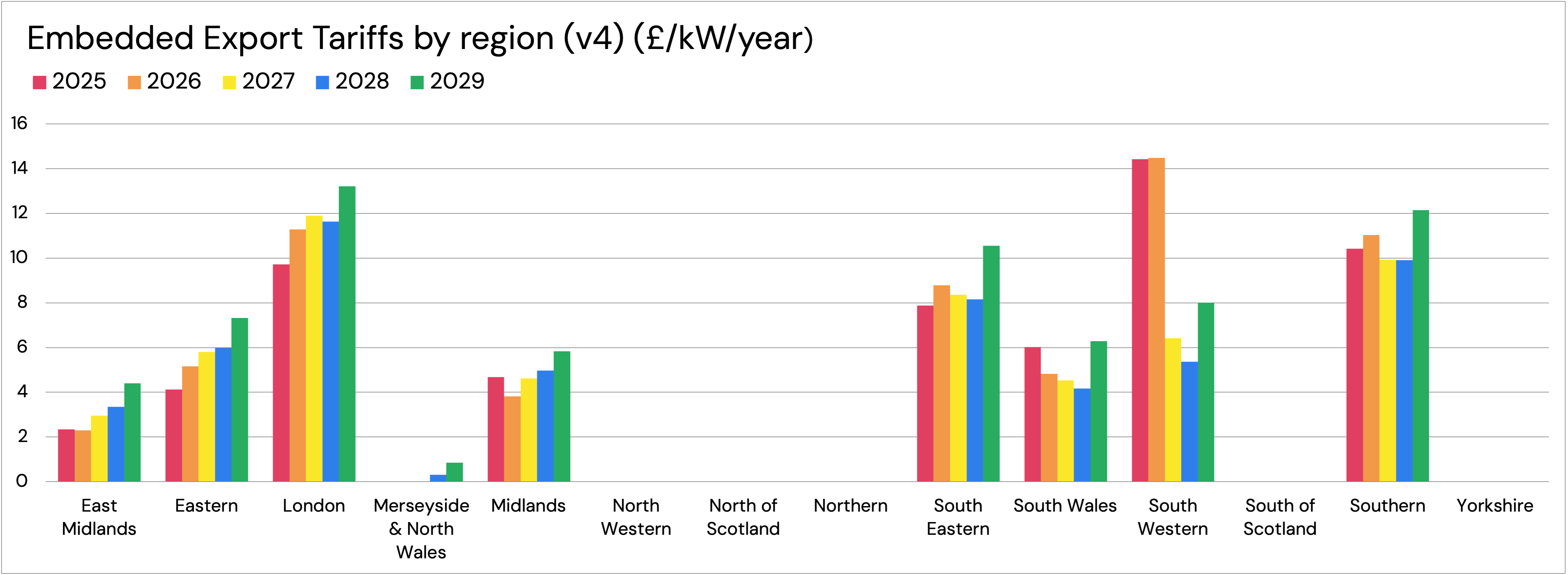
Embedded export tariffs vary from region to region
Depending on the Grid Supply Point (GSP), the amount that distribution-connected batteries are paid for exporting during Triads varies. We model Embedded Export tariffs using ESO’s five-year regional Transmission Network Use of System (TNUoS) charges. We assume that they remain stable from year 6 onwards.
In revenue curves, the benefit of TNUoS revenues from triads is smeared over the 12 month period, where a TNUoS charging year runs from April to March.
We assume no site imports during Triads
We assume sites don’t import during Triads—so you don’t pay import flexible TNUoS (which everyone, distribution or transmission connected, pays if they import). If the site does import during Triads, it can be expensive.
We assume a capture rate for export revenues dependent on battery duration
Analysis over the past 2 winters of the battery fleet’s success in hitting triad periods is available for 2023/2024 and 2022/2023 on the Modo platform.
Given this historic performance, we assume that 1h systems achieve 33% of the total possible triad revenue, and 2h systems achieve 85%.
For durations between these values, we apply a linear fit, and no system can capture more than 100% of triad revenues.
Wider generation TNUoS forecasts
BESS sites that are transmission connected or of capacity ≥100MW face wider generation TNUoS charges. These are flat rates that a site must pay each year.
Wider Generation TNUoS charges feature in both the Run Library and in Custom Runs.
Transmission-connected batteries pay fixed TNUoS
Export rates for transmission-connected generation have shifted from time-of-use (via the Triad mechanism) to a fixed rate via the Wider Generation tariffs. This is a result of the Targeted Charging Review.
The rate can be positive or negative and varies throughout the country. See Figure 4 here.
Example: Transmission-connected battery in South Wales
Let’s model a transmission-connected battery site in South Wales, due to come online during 2028. Transmission-connected batteries fall into the ‘Conventional Carbon’ generating class for TNUoS calculations.
The calculation for the Wider TNUoS tariff, Conventional Carbon, is:
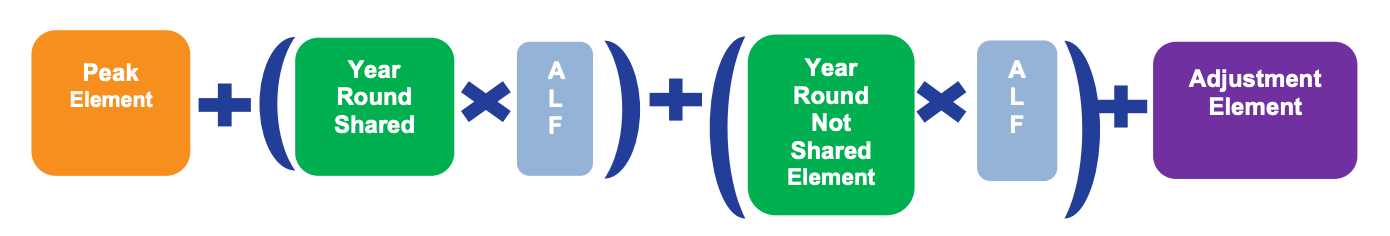
Taking numbers from the 5-year view of TNUoS tariffs, in the year 2028/2029 (p.14) and assuming the site has no historical data, we use an Annual Load Factor (ALF) generic for storage of 1.6301% (p.71).
This gives the calculation:
6.711930 + (- 7.300407 x 1.6301%) + (0 x 1.6301%)+ - 2.997585 £/kW = 3.5953 £/kW (to 4 significant figures), or £3595/MW/year.
We use ESO Wider Generation TNUoS forecasts
The Electricity System Operator has produced Wider Generation TNUoS forecasts for 2025-2029.
We use these and push the final value forwards for the rest of the forecast horizon, depending on the Generation Zone of a site.
Wider Generation TNUoS in the Modo Forecast
Tariffs are given per Generation Zone:
In the run library, users can pick the distribution region of their run. DNO regions have a many-to-many relationship with generation zones, so we have used the following mapping for simplicity:
| Distribution Network Region | Assumed Generation Zone |
|---|---|
| East Midlands | South Lincolnshire and North Norfolk |
| Eastern | Mid Wales and The Midlands |
| Merseyside & North Wales | North Midlands and North Wales |
| Midlands | Mid Wales and The Midlands |
| North Western | North Lancashire and The Lakes |
| North of Scotland | North Scotland |
| Northern | North East England |
| South Eastern | Essex and Kent |
| South Wales | South Wales & Gloucester |
| South of Scotland | Lothian and Borders |
| Southern | Somerset and Wessex |
| Yorkshire | South Lancashire, Yorkshire and Humber |
| South Western | West Devon and Cornwall |
| London | Central London |
Specific generation zones are available via custom runs.
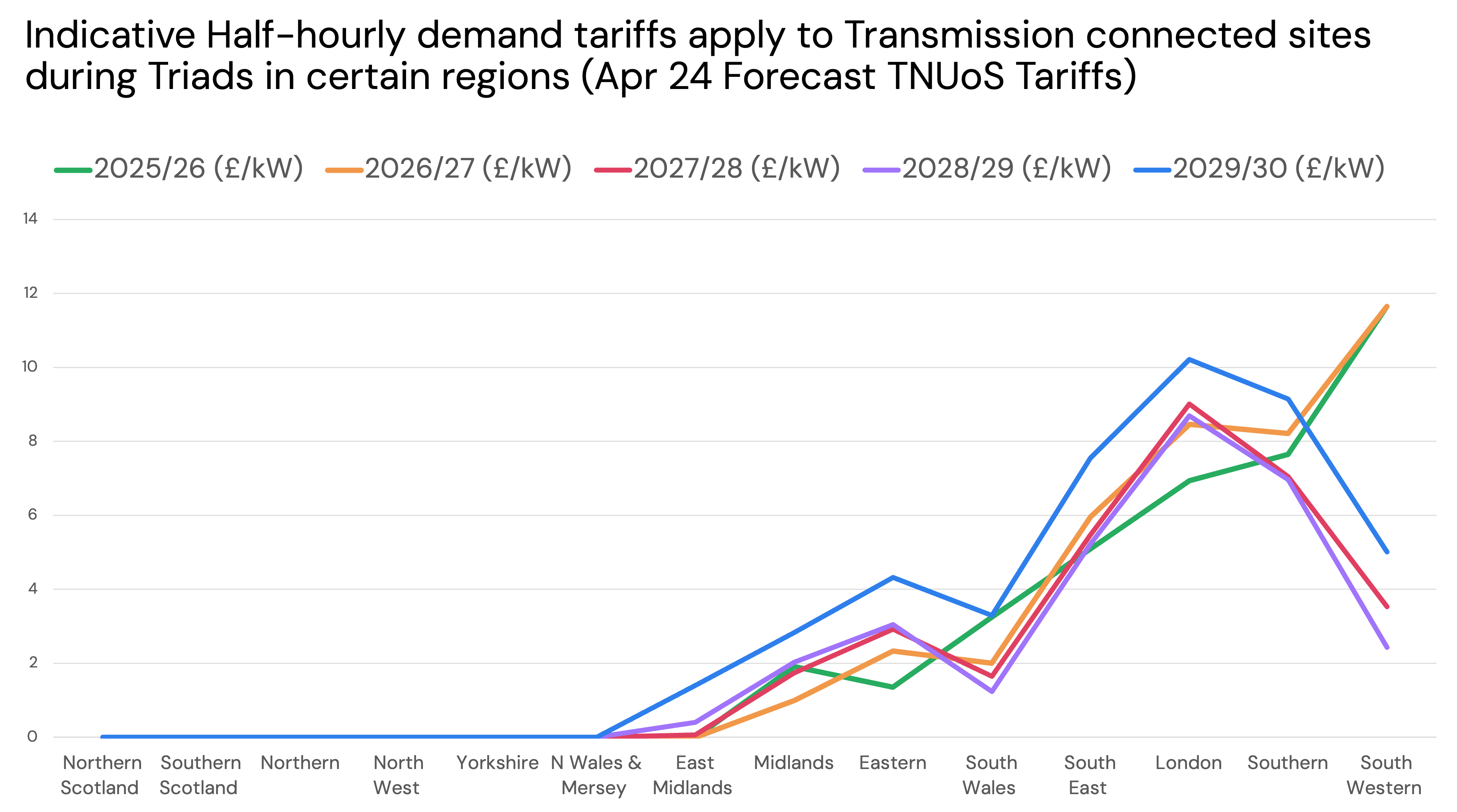
Half-hourly demand tariffs
Transmission-connected assets that import during triad periods will also be subject to Half Hourly Demand Tariffs. These vary depending on the region.
Note: In the Modo forecast for GB, we assume that no battery will import during a triad period. Thus we do not factor in the cost of this demand tariff in our TNUoS revenues.
The TNUoS charging regime is slightly complicated for batteries. It depends on if the site is transmission- or distribution-connected, where it is, and what it does during Triad periods.
- Generally, if you import during a Triad, you’ll pay
- If you export during a Triad, you might get some revenue depending on where the site is, according to Embedded Export tariffs
- If the site is larger than 100MW or connected directly to the transmission network, you also face fixed-cost Wider Generation tariffs
Note: All costs (or revenues) we display in our forecast numbers are purely for the battery on a site. Batteries on co-located sites will be subject to different TNUoS revenues.
TNUoS Overview
| Grid connection | Import (demand) | Export (generation) |
|---|---|---|
| Distribution | Fixed cost: £0 for batteries due to final demand exemption Flexible (Triad) cost: £ avoidable, (and smaller than it used to be) as per network rates |
Fixed cost: £0 Flexible (Triad) cost: £ avoidable, as per Embedded Export rates. £0 for Scotland, Northern, North West & Yorkshire |
| Transmission or embedded > 100MW assets | Fixed cost: see export Flexible (Triad) cost: £ avoidable: Set by half-hourly demand tariff |
Fixed cost: £+/- set by wider generation tariffs, and annual load factor (ALF) calculation Flexible (Triad) cost: £0 |
Batteries connected to the distribution network are exempt from TNUoS fixed import fees (provided they submit a Non-Final Demand form to NGESO).
All batteries (distribution or transmission) are exposed to flexible TNUoS charges if they import during a Triad, according to import rates (Figure 2 here). Distribution-connected assets get paid flexible TNUoS rates depending on where they are and their average power over Triad periods, according to Embedded Export Tariffs (shown below).
Transmission-connected assets are subject to fixed-cost TNUoS charges as per the Wider Generation tariffs. They can be positive or negative. Annual load factors are used in the calculation of these charges. For batteries without three years of historical data, the generic Annual Load Factor (ALF) is 1.63% (source).
Transmission-connected assets that import during triad periods will also be subject to half hourly demand tariffs (see figure above).